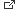Cashew Nut Anacardium occidentale

Cashews ready for harvest.
- Common Names
- Cashew Nut , Cajueiro, jambu
- Botanical Name
- Anacardium occidentale
- Family
- Anacardiaceae
Medicinal Uses & Benefits of Cashew Nut
![]() How to Use|
Side Effects |
Plant & Garden|
How to Use|
Side Effects |
Plant & Garden|
- Medicinal Uses: * Nutrition
* South_American
- Properties: * Astringent * Hypoglycemic * Vermifuge
- Parts Used: bark, stems, nuts, and resin
- Constituents: alpha-linolenic-acid ,anacardic-acid,arginine ,ascorbic-acid, benzaldehyde,beta-carotene ,beta-sitosterol,calcium ,gallic-acid ,palmitic-acid ,oleic-acid ,riboflavin, salicylic-acid ,selenium,tocopherol ,vanadium ,zinc
How to Use: Cashew Nut
Cashew nuts could possibly hold answers in the search for better ways to treat diabetes and high blood sugar. Animal studies with diabetic rats fed nut milk extract are promising, but more study is needed. 1 Anacardiaceae spp have long been used in the folk medicine and traditional cuisines of India, South America and the Caribbean. Cajueiro,as the tree is known in Brazil contains naturally occurring analogs of the latest diabetes drugs without their potential for liver damage or weight gain. 2,3
Preparation Methods & Dosage :Cashew nuts should be eaten freely as part of a healthy diet. Cajueiro is available as a tincture. Follow dosing instructions from physician if taking for diabetes.
Cashew Nut Side Effects: The oil in the nut shell can cause skin irritation if it is not heated first to render the oil less caustic. Never eat cashews raw. They are not dangerous after being roasted in the shell.
Plant Description
- Flowers: pink-striped yellow flowers on long stems
- Plant type: Tropical evergreen tree - related to mango, poison ivy. Reaches heights of thirty feet. Thick truck, winding branches that often reach the ground
- Leaves:large oval leaves
- Fruit: The cajueiro "fruit" is actually a thickened stem, the true fruit contains red or yellow flesh surrounding the cashew nut. The nut is used for food, the bark, stems, nuts, and resin are used medicinally
- Preferred Habitat:Tropical, dry and sandy soils
- Flowering Season:
- Distribution:Tropical - Indigenous to Brazil
Regional Traditions :Central and South America *
- Inflammopharmacology. 2012 Jan 25. Anti-inflammatory and anti-hyperlipidemic effect of Semecarpus anacardium. NIH
The present study thereby establishes the antilipidemic and anti-inflammatory effect of the drug. Thus, by decreasing the alterations in the lipid metabolism and inflammatory status, the drug can effectively improve the insulin sensitivity in rats and can serve as an excellent drug in the treatment of Type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Balch, Phyllis A.,CNC. "Prescription for Herbal Healing", (2002)p.67
When using cajueiro for diabetes, patience is required. Lower blood sugars may not be observed for three to four weeks. However, blood sugar should be measured at least daily to make sure the combination of cajueiro and prescribed insulin and/or other medications does not lower sugars excessively.
- Dr. Duke's
Phytochemical and Ethnobotanical Databases