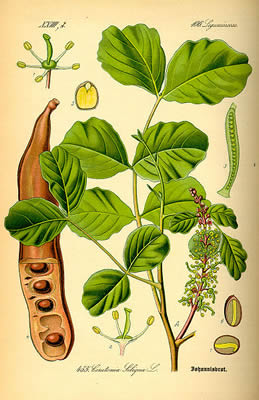
Carob Ceratonia siliqua

carob pods with leaves
- Common Names
- Carob , Locust Bean, St.John's-Bread
- Botanical Name
- Ceratonia siliqua
- Family
- FABACEAE
Medicinal Uses & Benefits of Carob
![]() How to Use|
Side Effects |
Plant & Garden|
How to Use|
Side Effects |
Plant & Garden|
- Medicinal Uses: * Children
* Culinary/Kitchen
* Diabetes
* Herbal Teas
- Properties: * Antitussive * Astringent * Hypoglycemic
- Parts Used: Seed Pod
- Constituents: arginine, benzoic-acid , gallic-acid , glucose , pectin ,starch, sucrose ,tannin,tocopherol,tyrosine
How to Use: Carob
Carob is a healthy substitute for chocolate that is lower in calories. Roasted carob is naturally sweeter, (or not as bitter), as unsweetened chocolate, so it can be made palatable with less added sugar in recipes. Carob has a number of advantages over chocolate: it is hypoallergenic, and hypoglycemic. 1 The true trick to enjoying carob is to not expect it to taste exactly like chocolate,(and be forever disappointed), but to learn to appreciate carob for its own unique taste.
Preparation Methods & Dosage : Carob powder and extracts can be substituted in place of cocoa in many recipes. Carob also makes a great tasting tea, alone or as a component of tea blends.
Carob Remedies
Carob Side Effects: None noted
Plant Description
- Fruit/Seeds:Small, numerous flowers, in catkin-like racemes. The fruit is an elongated pod, Carob consumed by humans is actually the dried (and sometimes roasted) pod, and not the 'nuts' or seeds.
- Plant Class:Dioecious (having separate male and female plants, flowering evergreen shrub or tree growing up to 30 ft tall.
- Leaves:4 to 8 inches long, pinnate leaves, broad-semi-spherical crown.
- Preferred Habitat:Drought resistant
- Flowering Season:Sept-October
- Distribution: native to the Mediterrianian, carob has been naturalized in the West including Florida and California.
History and Traditions & Folklore
Carob was eaten in Ancient Egypt, Rome and figures in passages from both the bible and the Talmud.CAROB-TREE, or Ceratonia siliqua, is a small tree of the Mediterranean coasts. It furnishes the St. John's Bread which probably corresponds to the husks of the Prodigal Son parable, and the seed which is said to have been the original jewellers' carat weight.Grieve, Margaret (2012-03-15). A Modern Herbal, Vol. I: 1 (Kindle Locations 6589-6592). Dover Publications. Kindle Edition.
- Hoffmann, David . "Medical Herbalism: The Science and Practice of Herbal Medicine" Healing Arts Press, (2010-12-15) Noncellulosic types of dietary fiber (such as carob gum, guar gum, and high-molecular-weight galactomannans from Ceratonia siliqua and Cyamopsis tetragonolobus) reduce intestinal absorption of glucose by slowing gastric emptying