Henna Lawsonia inermis

Woman's hand with henna design and Frangipani bouquet
- Common Names
- Henna , Henna or Hina
- Botanical Name
- Lawsonia inermis
- Syn. syn. L. alba
- Family
- Lythraceae
Medicinal Uses & Benefits of Henna
![]() How to Use|
Side Effects |
Plant & Garden|
Folklore
How to Use|
Side Effects |
Plant & Garden|
Folklore
- Medicinal Uses: * Ayurvedic
* Hair
- Parts Used: powdered leaves
- Constituents: hennotannic acid
How to Use: Henna
Henna, Lawsonia inermis,is a natural hair colorant that produces a red-orange dye molecule, lawsone. Henna contains hennotannic acid which, when mixed with hot water, will coat the hair. It seals in oils and tightens the hair cuticle giving your hair a rich, healthy shine. Henna has no lightening action, so the shade that you choose will depend on your hair color (natural or tinted) and it must be noted that Henna will not work as a colorant if your hair has more than 10% gray. Its effects will last up to 3 months. 1
Preparation Methods & Dosage :Powdered henna leaves form a base for body art and natural hair dyes. Follow product instructions for hair coloring.
Henna Side Effects: Some premixed pastes have been found to include: silver nitrate, carmine, pyrogallol, disperse orange dye, and chromium. These have been found to cause allergic reactions, chronic inflammatory reactions, or late-onset allergic reactions to hairdressing products and textile dyes. Buy only organically grown, pure henna from reputable sources. Avoid "Black" Henna boosted with PPD (para-phenylenediamine), it can cause lifelong health damage.
Plant Description
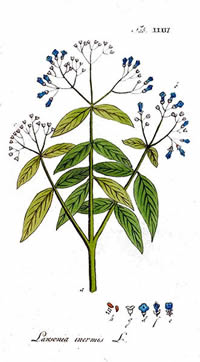
Botanical Illustration Adolphus Ypey 1813
- Flowers: Four sepals and a 2 mm calyx tube with 3 mm spread lobes. Petals are ovate, white or red stamens inserted in pairs on the rim of the calyx tube
- Plant Class:Desert Shrub: glabrous, multibranched with spine tipped branchlets
- Leaves: opposite, entire, glabrous, sub-sessile, elliptical, and broadly lanceolate
- Fruit: Fruits are small, brownish capsules, 4�8 mm in diameter, with 32�49 seeds per fruit
- Preferred Habitat:Desert and semi-arid zones
- Flowering Season:
- Distribution:tropical and subtropical regions of Africa, southern Asia, and northern Australasia in
Regional Traditions :Ayurvedic * Middle East *
History and Traditions & Folklore
Bridal couples in India decorate their hands and feet with intricate henna body art, referred to as Mehandi patterns. 2The earliest text mentioning henna in the context of marriage and fertility celebrations comes from the Ugaritic legend of Baal and Anath , which has references to women marking themselves with henna in preparation to meet their husbands, and Anath adorning herself with henna to celebrate a victory over the enemies of Baal. 2











