Guarana Paullinia Cupana

Guarana powder
- Common Names
- Guarana
- Botanical Name
- Paullinia Cupana
- Family
Medicinal Uses & Benefits of Guarana
![]() How to Use|
Side Effects |
Plant & Garden|
How to Use|
Side Effects |
Plant & Garden|
- Medicinal Uses: * Cellulite
* Diet/weight Loss
* South_American
- Properties: * Appetite Depressant * Astringent * Nervine * Stimulant
- Parts Used: seeds
- Constituents: guaranine (caffeine), theobromine, theophylline
How to Use: Guarana
Guarana is made from the seeds of the Brazil native Paulinia Cupana plant. Guarana is used traditionally to enhance energy levels. You will see this herb in many weight loss formulas listed as a thermogenic stimulator. Guarana seeds contain guaranine, which acts in a similar fashion to caffeine, and may be considered for all extents and purposes to be caffeine. Guarana can be used to help depress appetite for dieters, and can be very effective if you are prone to nervous headaches. Use this stimulating herb with common sense, I find a little goes a long way. Guarana is used in traditional medicine by the indigenous peoples of the Amazon region according to Ms. Grieve.
Nervine, tonic, slightly narcotic stimulant, aphrodisiac febrifuge. A beverage is made from the Guarana sticks, by grating half a tablespoonful into sugar and water and drinking it like tea. The Brazilian miners drink this constantly and believe it to be a preventive of many diseases, as well as a most refreshing beverage.1
guaranine,the stimulant constituent of guarana is said to be chemically identical to caffeine, may actually be caffeine, making guarana the highest source of caffeine available in nature. Guarana seeds contain 2.5 times the amount of caffeine than coffee does. 2,3
Preparation Methods & Dosage :Guarana seed powder is taken in capsule form, or it can be added to herbal tea blends
Plant Description
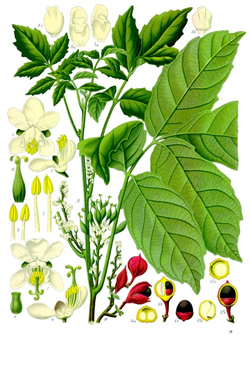
Koehler's Medicinal-Plants 1887
A native evergreen vine of the Amazon region, the guarana tree has orange to red berries that have been used like coffee in its native Brazil for centuries
Regional Traditions :Central and South America *
- Grieve, Maud Mrs. "A Modern Herbal" (1931)
- Mountain Rose Herbs
- Hoffmann, David (2010-12-15). Medical Herbalism: The Science and Practice of Herbal Medicine (p. 124). Healing Arts Press.











