Vanilla Vanilla planifolia
- Common Names
- Vanilla
- Botanical Name
- Vanilla planifolia
- Syn. Myrobroma fragrans (Salisbury); V. fragrans
- Family
- Orchidaceae
Medicinal Uses & Benefits of Vanilla
![]() How to Use|
Side Effects |
Plant & Garden|
How to Use|
Side Effects |
Plant & Garden|
- Medicinal Uses: * Culinary/Kitchen
- Properties: * Aromatic * Carminative
- Parts Used: Fruit (bean)
- Constituents: vanillin, vanillic-acid, tannin, sugars, sucrose, malic-acid, eugenol, fiber
How to Use: Vanilla
The long, slender black fruits of Vanilla planifolia are the vanilla “beans” that
are one of the most recognized and popular flavors in the world. The vanilla extract
we use in cooking comes from the vanilla orchid vine. While vanilla does not have any medicinal properties per se, it
does help to improve digestion. Vanilla is often
used to flavor less palatable herbal medicines.
Preparation Methods & Dosage :Whole vanilla pods can be used in teas and add flavor to sugar and coffees. Vanilla works well as an ingredient natural potpourri. You can make your own vanilla extract by soaking split vanilla pods in alcohol.
Vanilla Remedies
 In the Kitchen: Don't limit your use of vanilla to desserts,
but experiment with vanilla in stir frys and fish dishes for a unique flavor.
Each bean pod contains small, dot-like beans that can be scraped from the pod
with a knife. About 1 teaspoon of beans should be sufficient for most
recipes.
In the Kitchen: Don't limit your use of vanilla to desserts,
but experiment with vanilla in stir frys and fish dishes for a unique flavor.
Each bean pod contains small, dot-like beans that can be scraped from the pod
with a knife. About 1 teaspoon of beans should be sufficient for most
recipes.
Plant Description
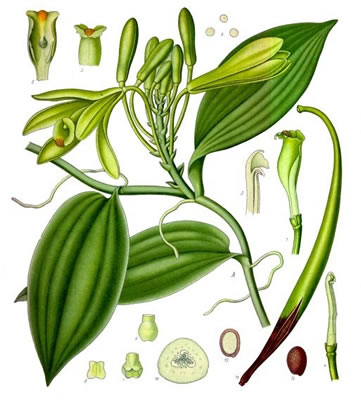
Kohler's Medicinal Plants 1857
Vanilla is is a stout, climbing orchid that grows in tropical evergreen forests by attaching itself to living trees. Orchid growers often train vanilla vine on a greenhouse wall. Vanilla is labor and time intensive, each flower must be hand pollinated to produce a vanilla pod.
- Flowers/Fruit/Seeds:Pale yellow-green flowers, followed by pendant capsules containing minute seeds
- Plant Class:Climbing evergreen perenial vine
- Rhizome:
- Leaves:Green, zig-zag stems, fleshly,oblong leaves
- Preferred Habitat:Thickets, tropical forests
- Flowering Season:Spring
- Distribution:Tropics and subtropics. Native to South America, the West Indies and Florida
Regional Traditions :Central and South America *












