Barberry, Common Berberis vulgaris L.

- Common Names
- Barberry , Huang Lian, Chinese Goldthread, Pepperidge-bush, Daru Haridra
- Botanical Name
- Berberis vulgaris L.
- Family
- BERBERIDACEAE
Medicinal Uses & Benefits of Barberry
![]() How to Use|
Side Effects |
Plant & Garden|
Folklore
How to Use|
Side Effects |
Plant & Garden|
Folklore
- Medicinal Uses: * Ayurvedic
* Candida/yeast
* Chinese
* Liver
* Psoriasis
- Properties: * Anti-inflammatory * Antibacterial * Bitter * Cholagogue * COX-2 Inhibitor * Hepatic
- Parts Used: bark, root-bark
- Constituents: alkaloids berberine, oxyacanthine, and columbamine
How to Use: Barberry, Common

Barberry can be used to
treat UTI's and yeast infections
Barberry is a traditional bitter tonic that helps support the liver functions and cleanse a congested system. 1 Barberry is rich natural source of berberine. Berberine is bright yellow and somewhat bitter, and has long been used in traditional medicine for its anti-inflammatory and anti-microbial effects. This well known antiseptic photochemical, also found in goldenseal and Oregon grape root, is used to treat a wide range of infections of the ears, eyes, mouth, and throat, staph and strep bacteria, each of which can commonly cause bacterial pinkeye. In fact Murine© eye drops contain berberine as the active ingredient.
Other common infections that can effectively be treated by barberry include yeast and bladder infections, and skin disorders, especially those like psoriasis that can benefit from a liver tonic.
Barberry has been used in traditional herbal medicine since early Egyptian times, when it was combined with fennel seed to prevent plague and treat fevers. These traditional historical uses are confirmed by modern science : Compounds in barberry inhibit the COX-2 enzyme.Whole herb extracts of barberry contain berberine as well as a supporting cast of chemicals that calm chronic inflammation. Compounds in barberry inhibit the COX-2 enzyme. Barberry and other berberine-containing herbs thus offer significant medical benefits for rheumatoid arthritis as well as cancers.2
Preparation Methods & Dosage :Liquid root extract is the most convenient way to use barberry. Must be used long term to see benefits. Follow dosage directions on bottle. Barberry root bark can be used in teas, tinctures, or incorporated in creams and lotions for external use.
Barberry, Common Remedies
Both Chinese goldthread (native to the mountains of Szechwan province in China) and the barberry known in Europe and North America are rich natural sources of berberine. 2
Ayurvedic Medicine
 Indian Barberry has the same main constituent, berberine, as the other species and in used in Ayurveda mainly for the liver.
Indian Barberry has the same main constituent, berberine, as the other species and in used in Ayurveda mainly for the liver.
Barberry, Common Side Effects:
Plant Description
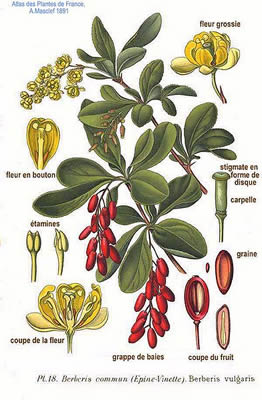
Atlas des plantes de France. 1891
- Flowers:Inflorescence long, drooping, many-flower racemes, of pale yellow flowers.
- Plant type: Attractive, bushy shrub grows to a height of from 3 to feet; the stem-wood, inner-bark and pith are yellow
- Leaves: Inversely egg shaped, short-petioled, closely serrate, and bristly-toothed.
- Fruit:
- Preferred Habitat:
- Flowering Season:May to June
- Distribution:Indigenous to Great Britain and other parts of Europe, and is becoming quite thoroughly naturalized here, especially in the Eastern States, cultivated as an ornamental 1
Regional Traditions :Ayurvedic * North America * Traditional Chinese Medicine *
How to Grow Barberry, Common
Barberry bushes are a low maintenance ornamental shrub that can add color to your landscape. Widely available at plant nurseries.
History and Traditions & Folklore
Berberis was well known to the ancients as a medicine, a dietetic for the sick, and a dye. As a drug it was steeped in beer and given to patients suffering from jaundice, as well as to check hemorrhages. Its popular use as a remedy barberry bark and cider was held in all forms of abdominal inflammation, but especially those accompanied with hepatic derangement and jaundice. 3The yellow root was used by Native Americans as a dye for fabrics as well as its widespread use in medicines. Barberry root tea was used to treat ulcers, sores, rheumatism and kidney ailments. 4
“Among the Italians, the Barberry bears the name of Holy Thorn, because it is thought to have formed part of the crown of thorns made for our Saviour.” (Grieve, Margaret)
 Mars owns the shrub, and presents it to the use of my countrymen to purge their bodies of choler. The inner rind of the Barberry-tree boiled in white wine, and a quarter of a pint drank each morning, is an excellent remedy to cleanse the body of choleric humours, and free it from such diseases as choler causes, such as scabs, itch, tetters, ring-worms, yellow jaundice, boils
Mars owns the shrub, and presents it to the use of my countrymen to purge their bodies of choler. The inner rind of the Barberry-tree boiled in white wine, and a quarter of a pint drank each morning, is an excellent remedy to cleanse the body of choleric humours, and free it from such diseases as choler causes, such as scabs, itch, tetters, ring-worms, yellow jaundice, boils
Nicholas Culpeper, 1653
- Hoffmann, David . Medical Herbalism: The Science and Practice of Herbal Medicine , Healing Arts Press, (2010): , 533
- Newmark, Thomas M. . Beyond Aspirin , , (2000): , p57
- Charles F. Millspaugh . American Medicinal Plants , , (1892): , p15
- Alma R. Hutchens . A Handbook of Native American Herbs , Shambahala, (1970): , p14
- Grieve, Margaret . A Modern Herbal, Vol. , Dover, (1931): ,












